Abstract
Introduction: Acquired or immune-mediated thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (aTTP) is a life-threatening thrombotic microangiopathy characterized by severe thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and organ ischemia. Inhibitory autoantibodies cause a severe deficiency of the von Willebrand factor (vWF) cleaving enzyme ADAMTS13, leading to intravascular vWF-platelet aggregation and microvascular thrombosis. The mainstays of treatment are plasma exchange (PE) and immunosuppression. Caplacizumab, a bivalent Nanobody, targets the A1 domain of vWF, inhibiting the interaction between ultra-large vWF and platelets.
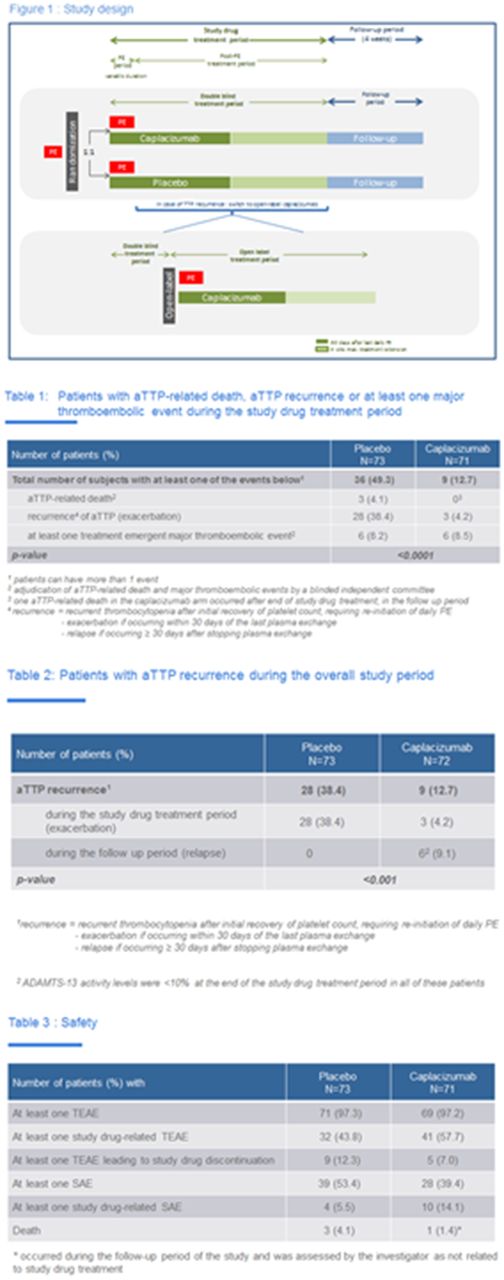
Methods: Patients with an acute episode of aTTP who had received one PE treatment were randomized 1:1 to placebo or 10 mg caplacizumab, in addition to daily PE and corticosteroids. A single IV dose of study drug was given before the first on-study PE and a SC dose was given daily during the PE period and 30 days thereafter. If at the end of this period there was evidence of ongoing disease, such as suppressed ADAMTS13 activity, investigators were encouraged to extend the blinded treatment for a maximum of 4 weeks together with optimization of immunosuppression. All patients entered a 28-day treatment-free follow up period after the last dose of study drug (Figure 1). Primary endpoint was time to platelet count response, defined as platelet count ≥ 150×109/L with stop of daily PE within 5 days. There were 4 key secondary endpoints, hierarchically ranked. The 1st was a composite of aTTP-related death, aTTP recurrence, or major thromboembolic event during the study drug treatment period. A blinded, independent committee adjudicated aTTP-related deaths and major thromboembolic events. The 2nd looked at recurrences during the entire study period, including the follow up period. The 3d evaluated refractoriness to therapy, defined as absence of platelet count doubling after 4 days of treatment and LDH still above normal. The 4th was the time to normalization of 3 organ damage markers: LDH, cardiac troponin I and serum creatinine.
Results: 145 patients were randomized, 73 to placebo and 72 to caplacizumab. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were balanced between groups, except for a higher proportion of initial episodes in the caplacizumab arm. Compared to patients treated with placebo, those on caplacizumab were >50% more likely to achieve a platelet response at any given time point (platelet count normalization rate 1.55, 95% CI 1.10 - 2.20, p <0.01). During the study drug treatment period, treatment with caplacizumab resulted in a 74% reduction in TTP-related death, recurrence of TTP, or a major thromboembolic event (p <0.0001, Table 1). During the overall study period, 28 patients in the placebo group experienced a recurrence versus 9 patients in the caplacizumab group, a 67% reduction (p <0.001, Table 2). In all 6 caplacizumab-treated patients with a relapse during the follow up period, ADAMTS13 activity was still <10% at stop of study drug, reflecting ongoing disease. No caplacizumab-treated patients were refractory to therapy, while 3 patients on placebo were (p =0.057). Treatment with caplacizumab was associated with a trend toward faster normalization of the 3 organ damage markers. Safety is summarized in Table 3. In the caplacizumab group, the most common study drug-related TEAEs were epistaxis, gingival bleeding, and bruising. During the study drug treatment period, 3 patients on placebo died. One death occurred during the follow up period in a caplacizumab-treated patient and was assessed by the investigator as not related to study drug.
Conclusions: Results of the Phase 3 HERCULES study confirm that treatment with caplacizumab reduces the time to platelet count response, resulting in faster resolution of aTTP. Treatment with caplacizumab also resulted in a highly clinically meaningful reduction in aTTP-related death, recurrence of aTTP, or a major thromboembolic event during study drug treatment. The relapses after stop of study drug in patients with ADAMTS13 activity <10% suggest that treatment should be continued until complete resolution of the underlying disease. Caplacizumab has a favorable safety profile, with mucocutaneous bleeding the most frequently reported AE. Caplacizumab, through rapid blocking of vWF-mediated platelet aggregation, represents a novel treatment option for patients with aTTP. (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT02553317)
Scully:Ablynx: Honoraria, Research Funding; Shire: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria; Alexion: Honoraria. Cataland:Ablynx NV: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Peyvandi:Ablynx, Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Ablynx, Bayer, Grifols, Novo Nordisk, Sobi: Speakers Bureau;Freeline, Kedrion, LFB, Octapharma: Consultancy. Coppo:Ablynx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Alexion: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Knöbl:Novo Nordisk: Consultancy, Research Funding; Shire: Consultancy, Research Funding. Kremer Hovinga:Baxalta/Shire: Other: unrestricted grant hereditary TTP registry; Ablynx NV: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Metjian:Ablynx NV, Shire, Omeros: Research Funding; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. de la Rubia:Amgen: Other: Honoraria; Celgene: Other: Honoraria; Janssen: Other: Honoraria. Pavenski:Alexion Pharmaceuticals: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Ablynx: Other: participation in industry sponsored RCT; CSL Behring: Research Funding. Callewaert:Ablynx NV: Employment. Biswas:Ablynx NV: Employment. De Winter:Ablynx NV: Employment. Zeldin:Ablynx NV: Employment.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal